Kosheeka
Kosheeka is a biotechnology company that specializes in manufacturing primary cells and stem cells for various applications with a focus on quality, and ethical practices.




How To Select Cancer Cell Lines For Your Experiments?
Before choosing cancer cell lines for your experiments, it’s essential to evaluate a few critical factors. Selecting the right cell line impacts the reliability and relevance of your results. Here are five key questions to consider to ensure that your chosen Cancer Cell Line is credible, contamination-free, biologically appropriate, genetically stable, and suitable for your specific experimental requirements.

Kosheeka
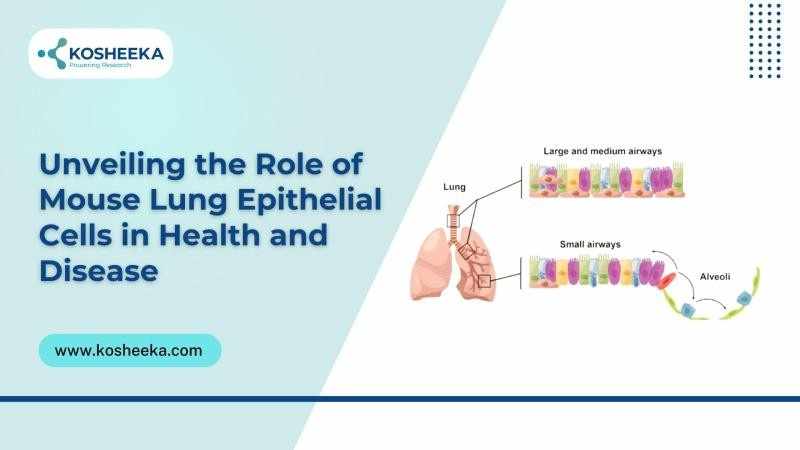

Unveiling the Role of Mouse Lung Epithelial Cells in Health and Disease
Mouse Lung epithelial cells are crucial for respiratory function. Located at the interface between the environment and the tissue, they act as protective shields. They also participate in fluid balance, immune response, surfactant synthesis, repair processes, particulate clearance, and disease pathogenesis. Due to the changes in the structure of the lungs during the respiratory cycle, they are exposed to mechanical stress. Due to their exposure to pathogens, they have become integral to research on understanding the pathophysiology of respiratory diseases, such as infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), asthma, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and infections such as COVID-19.

Kosheeka
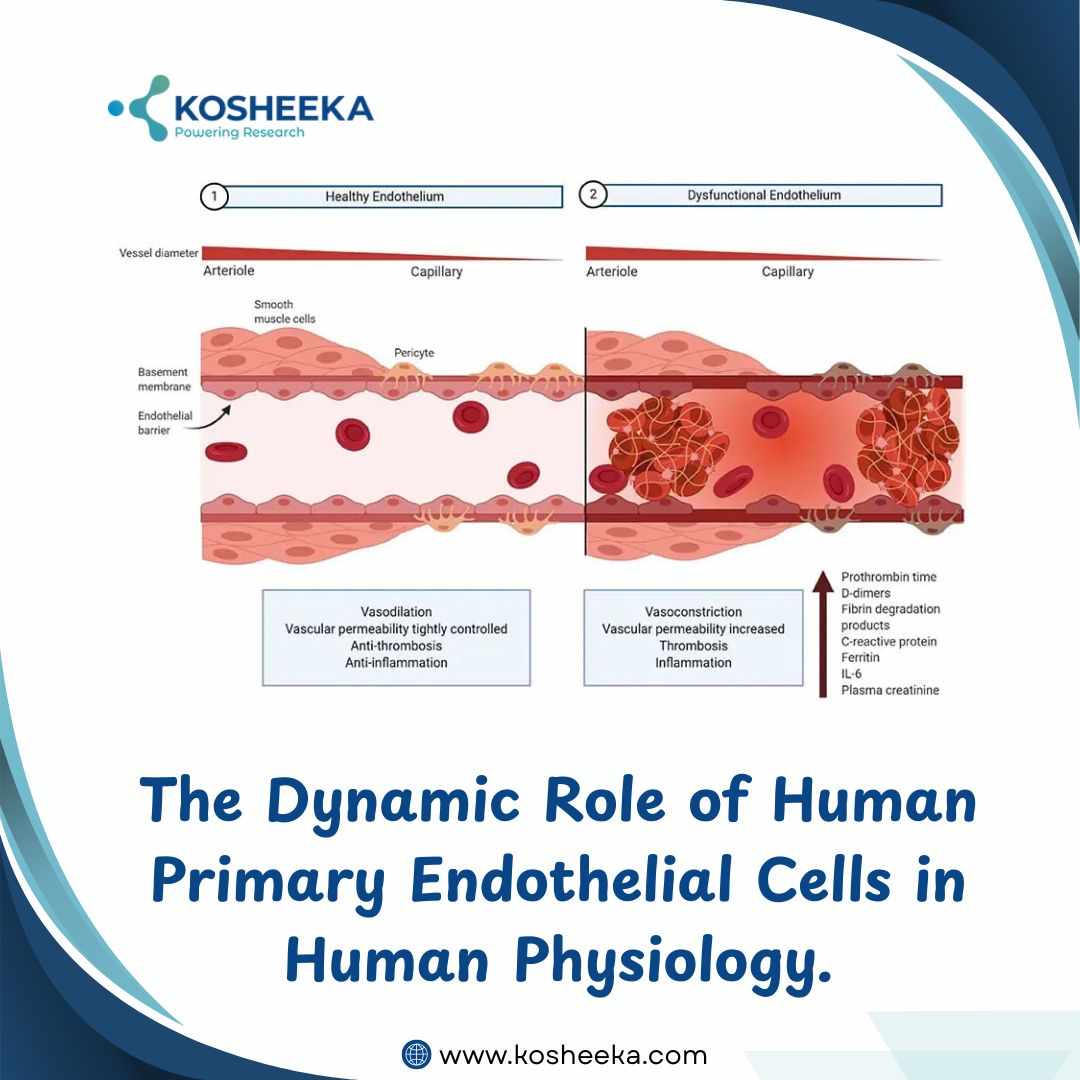

The Dynamic Role of Human Primary Endothelial Cells in Human Physiology
Human primary endothelial cells have been employed extensively in pathophysiology and therapeutic research. These cells are the basic unit of any blood vessel—capillaries, arteries, and veins. As a core component of the circulatory system, they are integrated into each organ. Their role extends from being a mere barrier to regulating tissue homeostasis, vessel integrity, disease pathogenesis, immune modulation, etc. The significance of endothelial cells in tissues has even led to their incorporation into 3D structures.

Kosheeka


Species-Specific Primary Cells: Enhancing In Vitro and In Vivo Research
Primary cells are the backbone of biomedical research. Species-specific primary cells have acquired focus from the scientific community owing to the use of animal models. They have accelerated the pace of research and provided valuable information. Their applications in diverse fields range from basic research to drug development. When comparing primary cells vs cell lines in species-specific in vitro culture, both types serve a distinct purpose. Researchers use them as per their study goals. This blog highlights the significance of species-specific cells and their applications.

Kosheeka
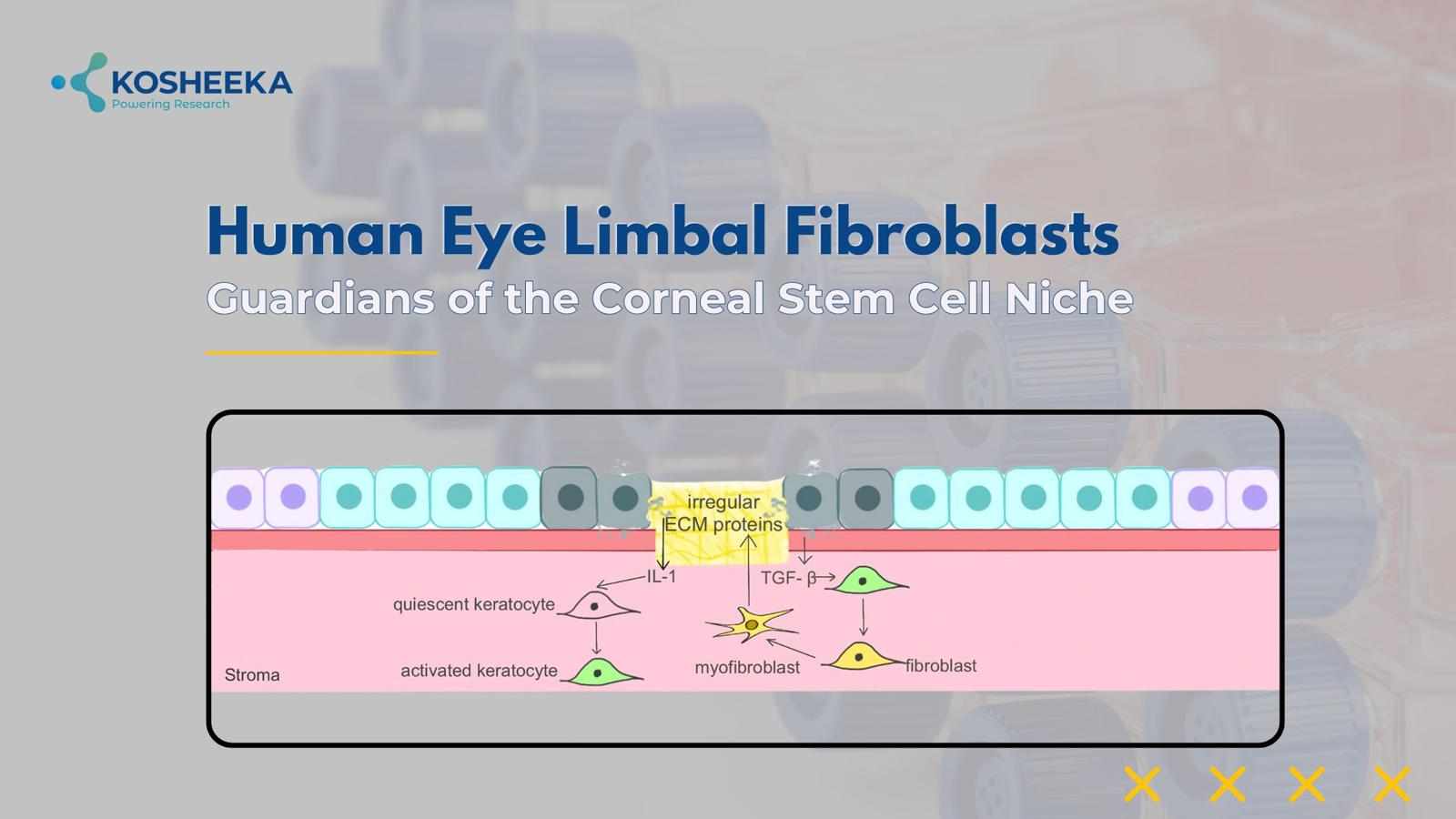

Human Eye Limbal Fibroblasts: Guardians of the Corneal Stem Cell Niche
Corneal blindness has affected more than 10 million lives on a global level. Cellular regeneration of corneal epithelium is a possible treatment option, prompting substantial research in the area. Human eye limbal fibroblasts have emerged as key cells in epithelial regeneration. They maintain the niche for corneal epithelial stem cells and repair tissue injury. Therefore, these cells have become a center for scientific investigation for developing novel therapeutics. This blog explores the biology, function, and therapeutic promise of primary human eye limbal fibroblasts in regenerative ophthalmology.

Kosheeka


Applications of Animal Cell Culture: The Foundation of Scientific Advancements
Animal cell culture refers to growing cells outside the body in a controlled environment. Although the practice began in the 1900s to observe the cellular events, it has progressed tremendously. Now it has grown in its techniques and applications. In comparison to in vivo studies, in vitro models have facilitated research in a time-efficient and cost-effective manner. It has drastically expedited research and drug development. This article details the applications of animal cell culture in biomedical research.

Kosheeka